Information About Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a virus that infects the skin, causing undesireable bumps or lesions to appear on the infected areas of the skin. The disease is very contagious, hence the name "contagiosum". The virus is transmitted from one person to the other through contact. This can be through touching the infected person directly, or by sharing clothing, pillows, towels, etc. with someone who is infected.

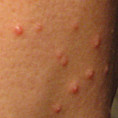
Appearance
Within two to four weeks of infection (or sometimes even more), tiny pearl shaped bumps start appearing on the infected skin. The bumps are whitish in color, smooth, and shiny, making them look lilke small pearly beads. They are raised a bit over the skin and can be felt easily by touch. Over the next few weeks, those bumps will transform into ugly-looking large red bumps, usually with a white tip. They are now significantly raised over the skin, giving your skin a bumpy feel.
Transmission
Molluscum contagiosum is very contagious, so you must handle it with care to avoid transmitting it to other people or even to other parts of your body. Simply rubbing the bumps and touching someone else with your fingers can infect them, especially if they have a weakened immune system, or you happen to touch them on a cut.
Dangers
Molluscum contagiosum is not considered a dangerous virus because it has no adverse effects or symptoms. It is mostly an annoyance, especially from a cosmetic perspective. The bumps, if visible, make people nervous and make the infected people very self-aware. Other than cosmetic annoyance, the bumps can be itchy at times. If scratched repeatedly, the surrounding skin can break and result in a more serious infection that may require medical attention. You should be extra wary with children because it may be difficult to convince them not to scratch. Scratching can cause a more serious infection, not to mention the fact that it will spread the virus even more.
FAQ
- Who is at risk of catching molluscum contagiosum?
Anyone can get infected with the virus, whether they are children or adults. Children are usually more at risk because they come in physical contact with others more often, and that is how the virus is transmitted. Adults, especially those with weakened immune systems tend to have it in their genital area due to physical contact during sex.
- Is molluscum contagiosum a sexually-transmitted disease?
No, but it can get transmitted during sexual intercourse due to physical contact. This is especially true for molluscum in the genital and pubic areas because of extended skin contact and rubbing in those regions during sex.
- What are the symptoms of molluscum contagiosum?
The virus does not have any known adverse symptoms or effects other than the ugly bumps and some occasional itching.
- If it itches, can I scratch?
NO! Sometimes the bumps will itch a bit, but it is important NOT TO SCRATCH. Scratching the bumps will spread the virus even more to surrounding skin. Plus, you now have the virus on your finger which can get infected, as well as infecting other parts of your body that your fingers touch. In addition, scratching can break the skin and cause a sore which can get infected with something else. So do no scratch. Do not even rub!
- Will the bumps last forever?
For most healthy people, the body's immune system will manage to eventually kill the virus. Without proper treatment, the infection can last anywhere from 9 months to two years or maybe more. Some individual bumps may fade on their own and get replaced by others on surrounding skin.
- Will the molluscum bumps scar?
It depends. If a bump is scratched until a sore forms, then it will probably leave a scar. Some treatments like liquid nitrogen or surgical removal will also leave a scar. If left on their own until the infection heals itself, then the bumps do not usually leave scars, although they will take several months to disappear completely.
- Should I seek medical help?
You need to see a doctor to make sure that the infection is actually molluscum contagiosum not something else that could be more dangerous. Once you confirm that you have molluscum contagiosum, your doctor may prescribe a course of treatment for you, or you can check out some other forms of treatments.
About Molluscum Contagiosum :: Molluscum Causes :: Molluscum Symptoms :: Molluscum Pictures
Molluscum Treatment :: Molluscum in Children :: Molluscum in Adults :: Genital Molluscum